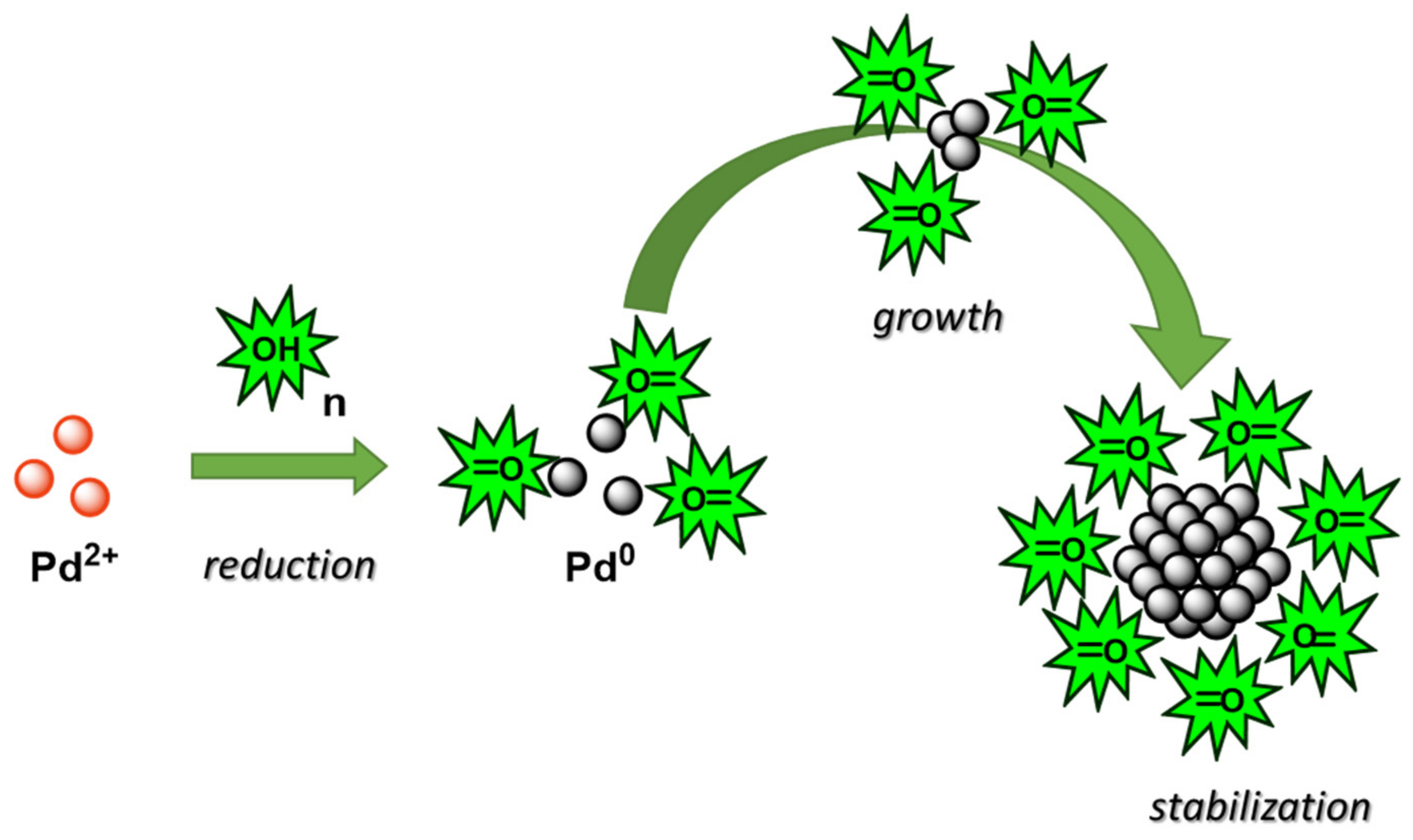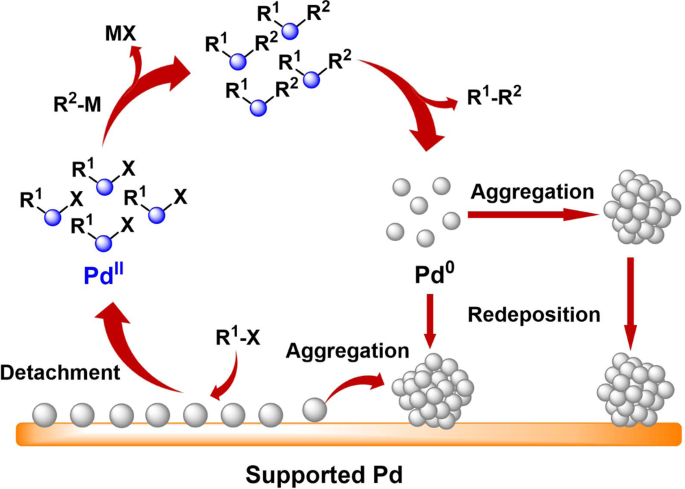
Enhancing stability by trapping palladium inside N-heterocyclic carbene-functionalized hypercrosslinked polymers for heterogeneous C-C bond formations | Nature Communications

Molecular Cage Impregnated Palladium Nanoparticles: Efficient, Additive-Free Heterogeneous Catalysts for Cyanation of Aryl Halides | Journal of the American Chemical Society

Palladium nanoparticle biosynthesis via Yerba Mate (Ilex paraguariensis) extract: an efficient eco-friendly catalyst for Suzuki–Miyaura reactions | SpringerLink

One-pot synthesis of bio-supported Pd nanoparticles by using clove leaf and their catalytic performance for Suzuki coupling reaction - ScienceDirect

Preparation scheme of phosphine bound Cell-OOCPhPPh2-Pd nanocatalyst,... | Download Scientific Diagram

Metal–Micelle Cooperativity: Phosphine Ligand-Free Ultrasmall Palladium(II) Nanoparticles for Oxidative Mizoroki–Heck-type Couplings in Water at Room Temperature | Semantic Scholar
Phosphine‑Functionalized Chitosan Microparticles as Support Materials for Palladium Nanoparticles in Heck Reactions | Request PDF
BJOC - Palladium nanoparticles supported on chitin-based nanomaterials as heterogeneous catalysts for the Heck coupling reaction

PDF) Palladium nanoparticles supported in a polymeric membrane: an efficient phosphine-free “green” catalyst for Suzuki–Miyaura reactions in water

The Direct Non‐Perturbing Leaching Test in the Phosphine‐Free Suzuki–Miyaura Reaction Catalyzed by Palladium Nanoparticles - Kashin - 2015 - ChemCatChem - Wiley Online Library

Immobilizing biogenically synthesized palladium nanoparticles on cellulose support as a green and sustainable dip catalyst for cross-coupling reaction | SpringerLink
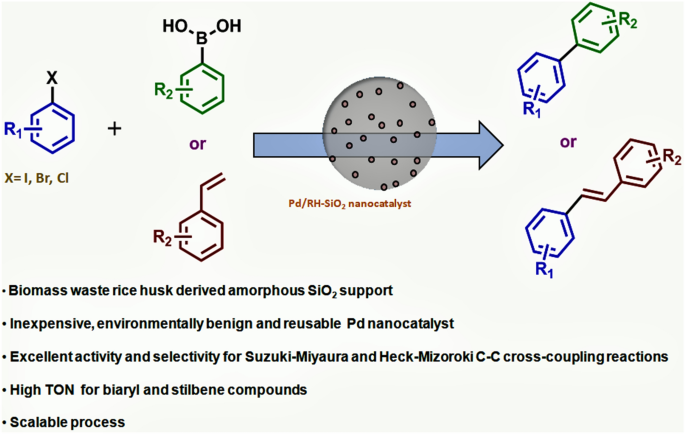
Biomass waste rice husk derived silica supported palladium nanoparticles: an efficient catalyst for Suzuki–Miyaura and Heck–Mizoroki cross-coupling reactions | SpringerLink
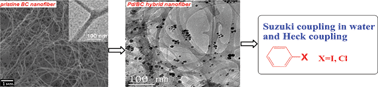
Bio-supported palladium nanoparticles as a phosphine-free catalyst for the Suzuki reaction in water - RSC Advances (RSC Publishing)

Deposition of Palladium Nanoparticles by the Coating of the Carbonaceous Layer from Wastepaper-Derived Bio-Oil | ACS Omega
![PDF] Biogenic synthesis of palladium nanoparticles and their applications as catalyst and antimicrobial agent | Semantic Scholar PDF] Biogenic synthesis of palladium nanoparticles and their applications as catalyst and antimicrobial agent | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/0fe235ad48084a74d275382bacd7cb6259ff092f/6-Figure1-1.png)
PDF] Biogenic synthesis of palladium nanoparticles and their applications as catalyst and antimicrobial agent | Semantic Scholar
Biogenic synthesis of palladium nanoparticles and their applications as catalyst and antimicrobial agent | PLOS ONE

Catalytic Properties of Unsupported Palladium Nanoparticle Surfaces Capped with Small Organic Ligands - Gavia - 2015 - ChemCatChem - Wiley Online Library
Palladium nanoparticle-decorated reduced graphene oxide sheets synthesized using Ficus carica fruit extract: A catalyst for Suzuki cross-coupling reactions | PLOS ONE
Palladium and Gold Perfluoro-Tagged Phosphine-Free Nanoparticles and Bio-Palladium Nanoparticles: New Catalysts for Organic Synt

Phosphine Ligand-Free Bimetallic Ni(0)Pd(0) Nanoparticles as a Catalyst for Facile, General, Sustainable, and Highly Selective 1,4-Reductions in Aqueous Micelles | ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces

Catalytic activity of biomass-supported Pd nanoparticles: Influence of the biological component in catalytic efficacy and potential application in 'green' synthesis of fine chemicals and pharmaceuticals - ScienceDirect
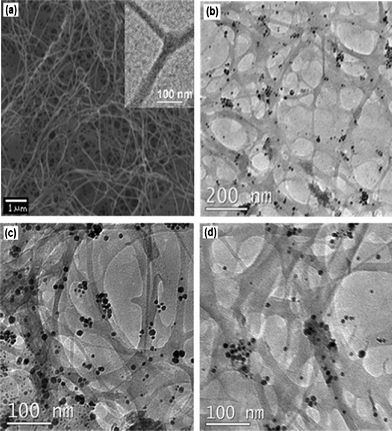
Bio-supported palladium nanoparticles as a phosphine -free catalyst for the Suzuki reaction in water - RSC Advances (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/C2RA01015A

Phosphine-Free and Reusable Palladium Nanoparticles-Catalyzed Domino Strategy: Synthesis of Indanone Derivatives | The Journal of Organic Chemistry
Biogenic synthesis of palladium nanoparticles and their applications as catalyst and antimicrobial agent | PLOS ONE